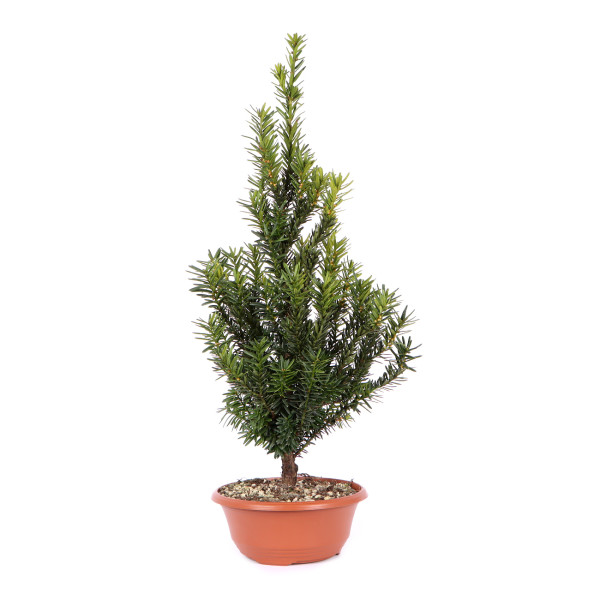
- Order number: 1813-P-25-0304
- Height: 55 cm (incl. pot)
- Foliage: evergreen
- Bonsai Pot: plastic pot
- Year: 2016
- Origin: Germany
Taxus x media ‘Hillii‘ - Anglojap Yew ‘Hillii‘ General: The anglojap yew was created in... more
Taxus x media ‘Hillii‘ - Anglojap Yew ‘Hillii‘
General:
The anglojap yew was created in the early 1990s from a cross between the European yew (Taxus baccata) and the Japanese yew (Taxus cuspidata). It has a dense and compact growth and with age a vase-shaped habit. The anglojap yew grows slowly and does not produce any fruit, as the variety emerged from the male form.
Care as a bonsai:
The anglojap yew can be cultivated for bonsai like an ordinary yew (see Taxus baccata). Due to the many shoots and the good branching, it has a good potential for this. Our anglojap yew trees are propagated from cuttings and therefore have no grafting point.
Viewed